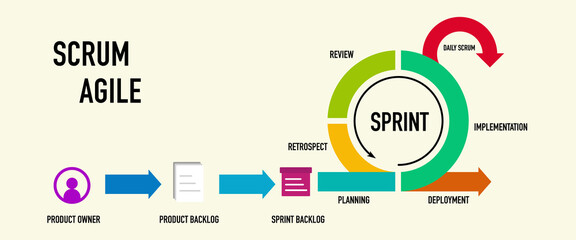
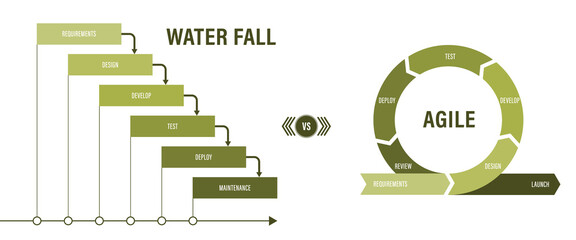
Agile Methodology
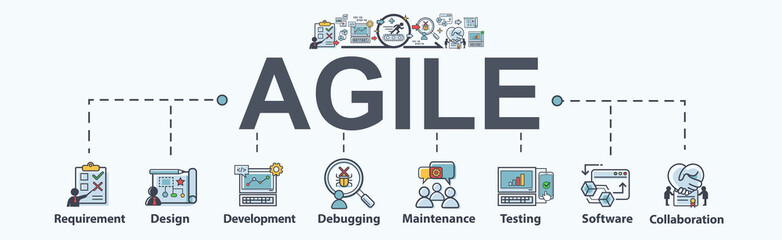
Agile is a software development approach that emerged in the late 1990s following the advent of methods such as rapid application development (RAD), extreme programming (XP) and the Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM – now known as the DSDM Agile Project Framework). The application of Agile methods evolved as a reaction to the perceived shortcomings of the linear development lifecycles, in particular, their emphasis on completing each stage before moving on to the subsequent stage.
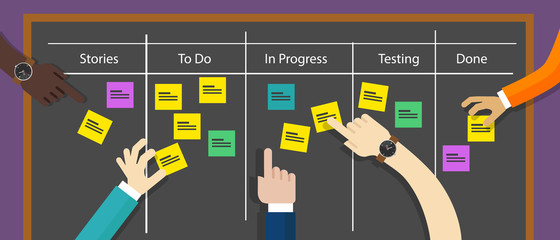
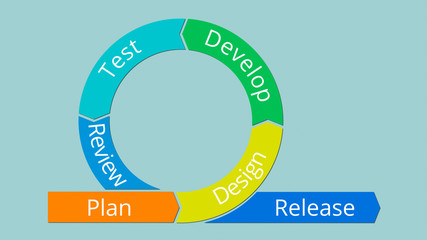
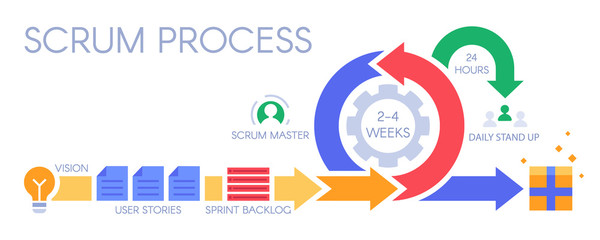
Agile methodologies have gained popularity in recent years due to their ability to adapt to changing requirements and deliver value to customers more effectively. In addition to the methods mentioned, other frameworks such as Scrum, Kanban, and Lean have also contributed to the Agile movement. The Agile approach emphasises the importance of self-organising teams, frequent customer collaboration, and the ability to respond to change over following a plan. This flexibility allows for continuous improvement and the incorporation of feedback throughout the development process. As businesses increasingly recognize the benefits of Agile, professionals in various roles, including project managers, developers, and quality assurance specialists, are honing their skills to align with Agile principles and practices. The Agile mindset encourages a shift from traditional, rigid processes to a more dynamic, adaptable approach, ultimately leading to greater customer satisfaction and higher quality software products.
The term ‘agile’ is a multifaceted concept that holds various interpretations within the agile community. It encompasses a collection of well-established frameworks known as ‘agile methods’ as well as recognized behaviours, concepts, and techniques that define the agile approach to work. However, due to its diverse nature, there is no singular definition of agile that can fully encompass all its facets. This breadth allows for flexibility and adaptation based on the specific needs and context of a project or organization. Ultimately, agile is a mindset that values collaboration, flexibility, and continuous improvement in order to deliver value to stakeholders.
The Agile Manifesto,
The Agile Manifesto, written in 2001, has had a profound impact on the software development industry, steering it towards a more collaborative and adaptive approach. Its four foundational values – individuals and interactions over processes and tools, working software over comprehensive documentation, customer collaboration over contract negotiation, and responding to change over following a plan – have provided a guiding light for countless teams and organisations seeking to improve their development processes. The principles behind the manifesto emphasise flexibility, continuous improvement, and customer satisfaction, fostering a culture of responsiveness and innovation within development teams. This shift in mindset has led to the widespread adoption of agile methodologies, such as Scrum and Kanban, and has influenced diverse domains beyond software development, including project management, marketing, and even non-profit organisations.
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools is a fundamental principle of the Agile Manifesto, emphasising the importance of human aspects in the development of software and in project management. This principle highlights the significance of effective communication, collaboration, and teamwork within a project, as well as valuing the capabilities and contributions of individuals over relying solely on processes and tools. It underscores the idea that while processes and tools are undeniably essential, the human element plays a crucial role in the success of any endeavour, shaping its culture and fostering innovation.
- Working software over comprehensive documentation is a fundamental principle of agile development, emphasising the importance of delivering a functional product over extensive written documentation. This shift in focus encourages teams to prioritise the continuous refinement and enhancement of the software’s features, fostering a culture of ongoing innovation and value creation. By placing a strong emphasis on the functioning product, agile teams can more readily engage in rapid prototyping and user feedback cycles, facilitating the incorporation of user preferences and evolving market dynamics into the software’s development process. This iterative approach not only enhances the team’s ability to swiftly adapt to changing requirements and technological advances but also supports the cultivation of a user-centric mindset, resulting in software solutions that closely align with the needs and expectations of their intended audience. Moreover, by promoting a proactive orientation toward tangible outcomes, the agile methodology inherently fosters a collaborative environment where cross-functional teams work in harmony to produce meaningful and impactful deliverables, further nurturing a sense of ownership and shared responsibility within the project.
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation is a fundamental principle in modern business practices. By emphasising the importance of working closely with customers, businesses demonstrate their commitment to understanding, addressing, and incorporating customer feedback. This approach fosters a strong sense of partnership between the business and its clients, leading to enhanced trust and loyalty. It also allows for a more dynamic and adaptable business model, where the evolving needs of the customers can be promptly accommodated. Moreover, prioritising customer collaboration sets the stage for long-term relationships, fostering a mutually beneficial environment where both parties can thrive and succeed together.
- Responding to change over following a plan is a key principle in agile project management. This approach emphasises the importance of remaining adaptable and flexible in the face of evolving requirements and circumstances. By prioritising responsiveness, teams can quickly adjust their course of action based on feedback and new information, fostering a more dynamic and efficient workflow. Embracing change as a natural and beneficial aspect of the project development process allows for timely problem-solving and continuous improvement, ultimately leading to greater success in delivering value to stakeholders.